Since 1976, Tufts CSDD has provided robust, objective evidence-based research, analysis, and insight, which have informed stakeholders throughout the drug development enterprise. Here are select Tufts CSDD research milestones during our 46+ year history:









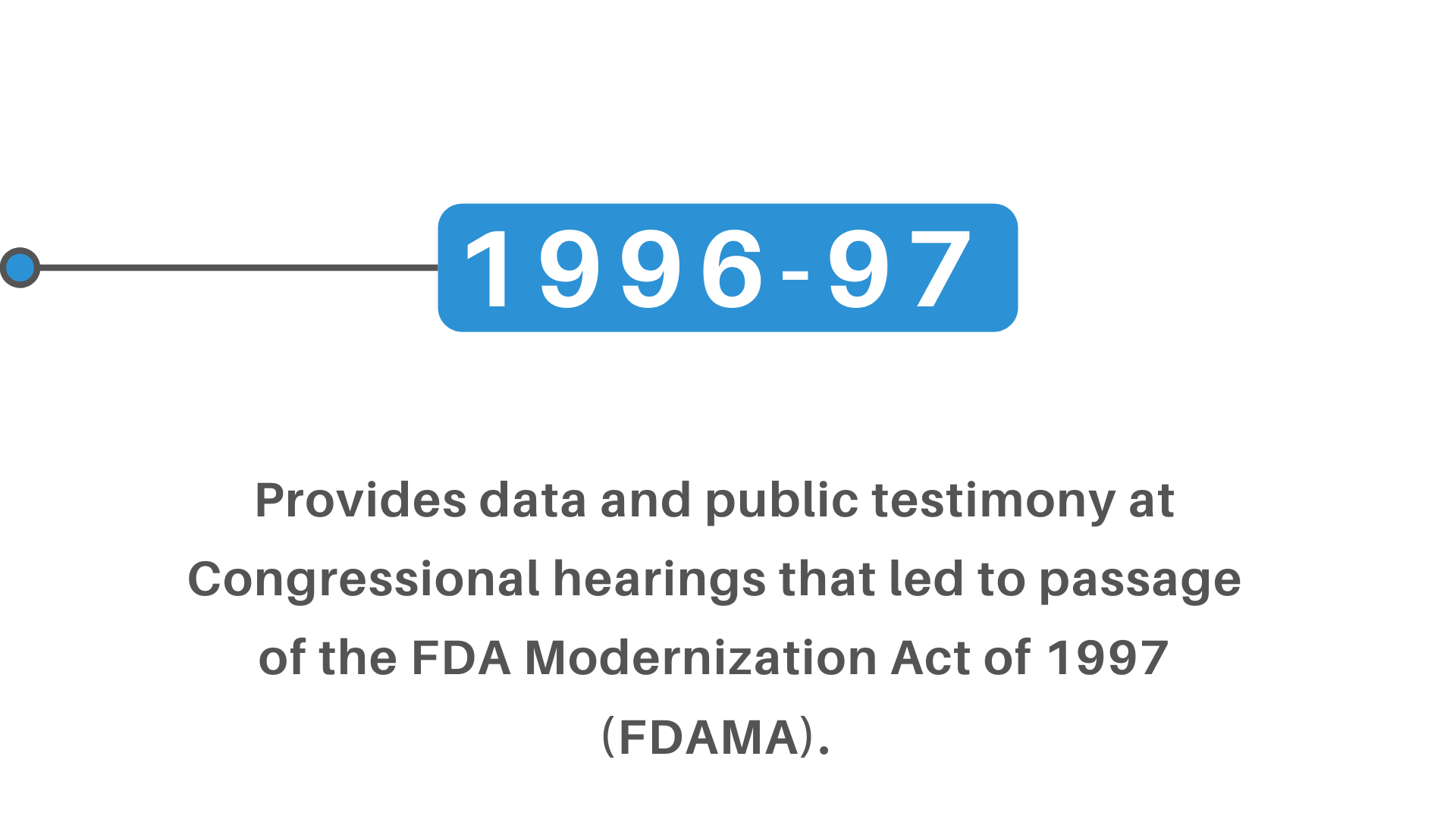



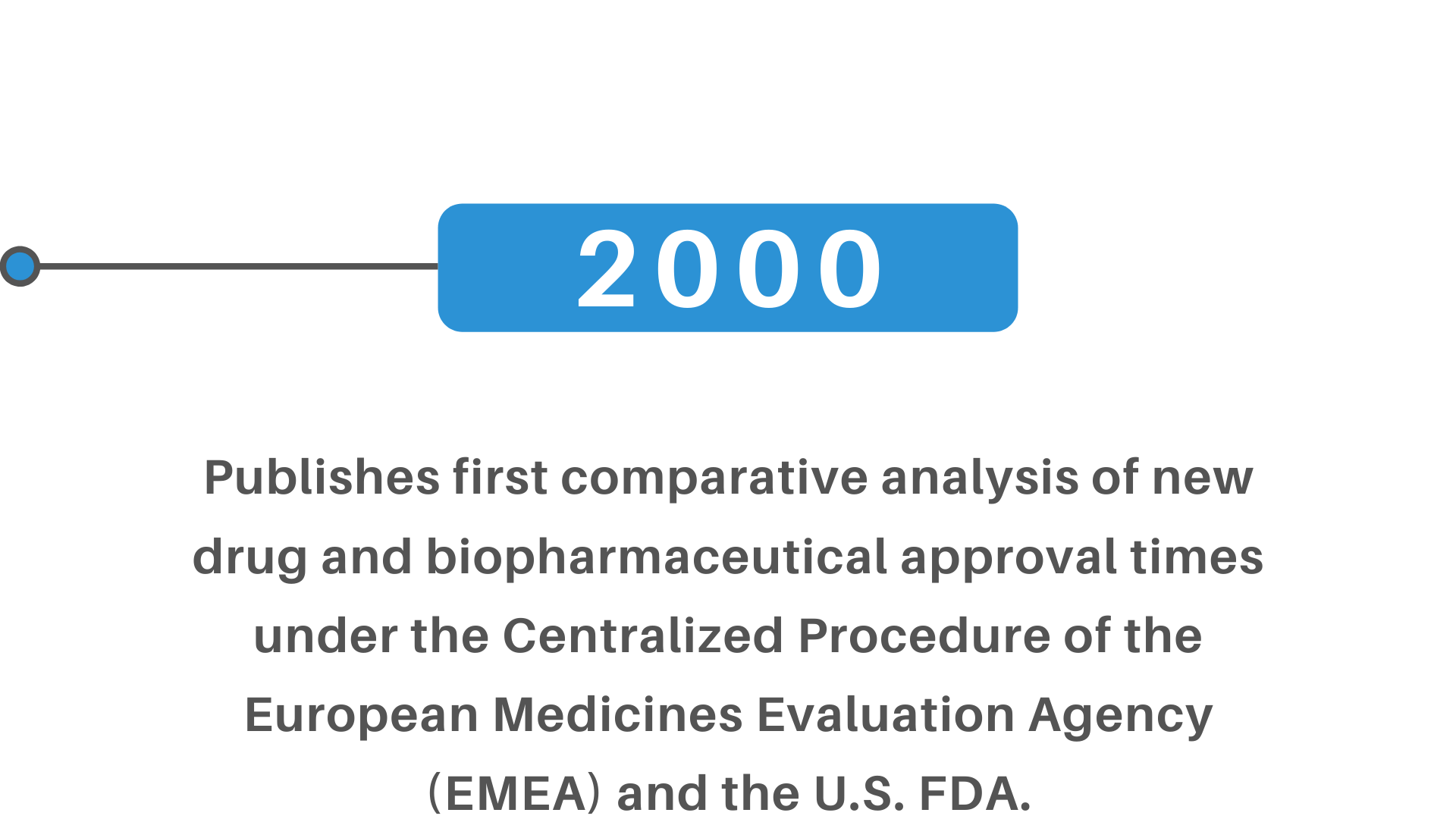







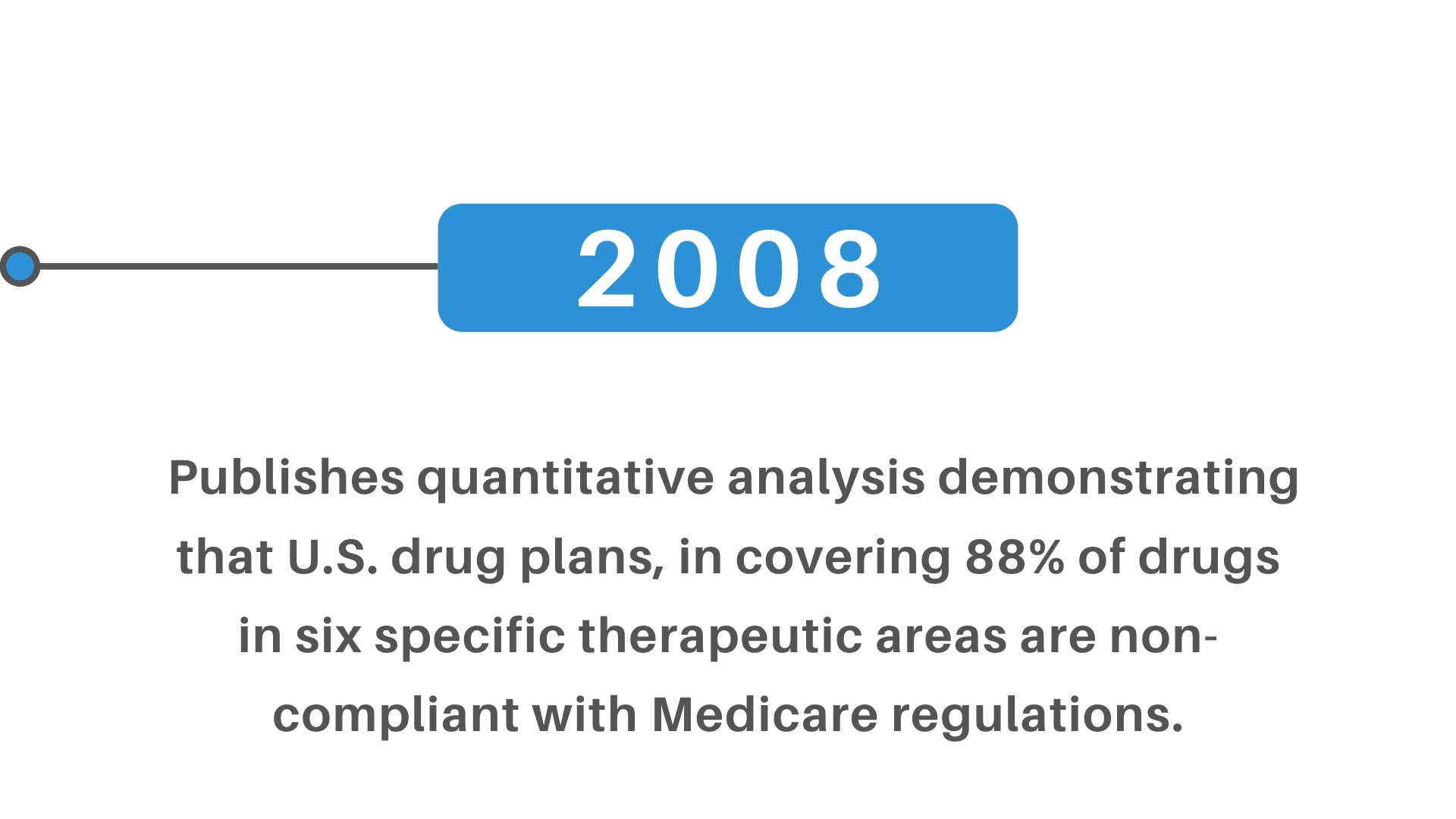

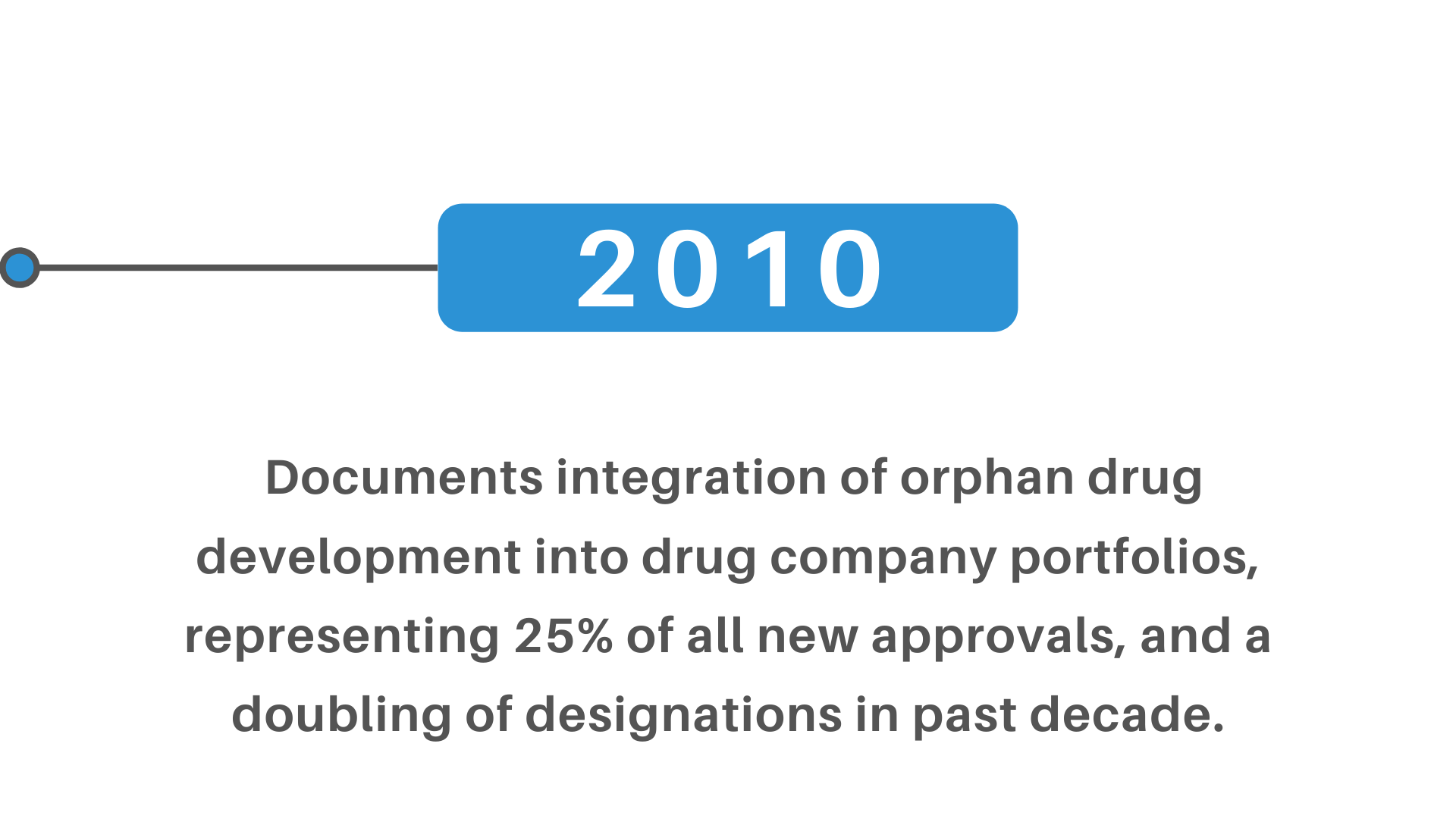




+(2)+regulatory+pathway+review+process+molecular+entity+approvals.png)





.png)
